
Mayumi KAJIMURA
-
- Research Field :
- Physiology
-
- E-mail :
-

-
- Specific Research Topic :
- Vascular Biology, Brain Metabolism, Neurovascular coupling
Research Description
RESEARCH INTERESTS:The role of gaseous mediators in the regulation of vascular functions and neural function in the central nervous system
Material
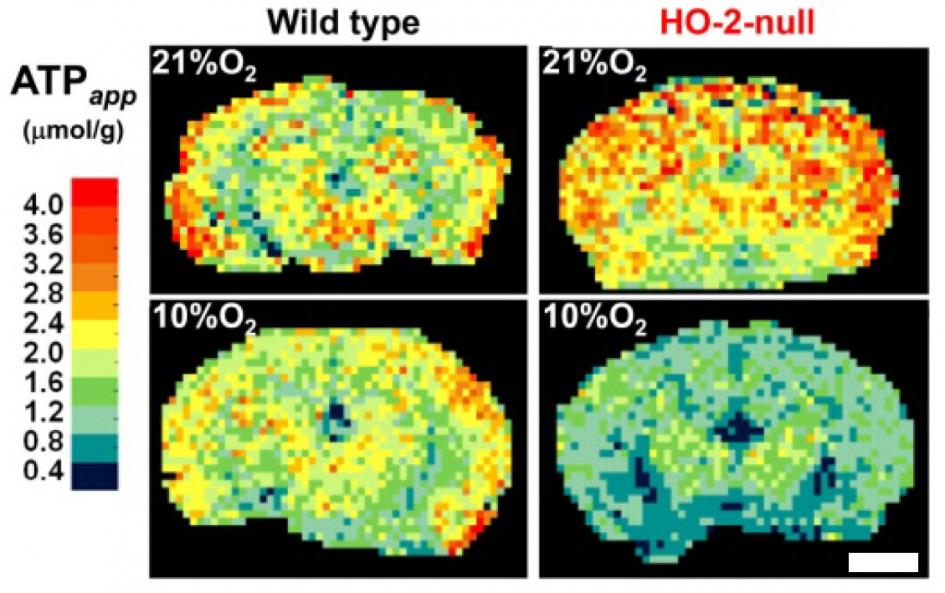
Energy metabolism of the mouse brain during ischemia (Click to enlarge the image)
Quantitative imaging mass spectrometry showing spatial distributions of ATP.
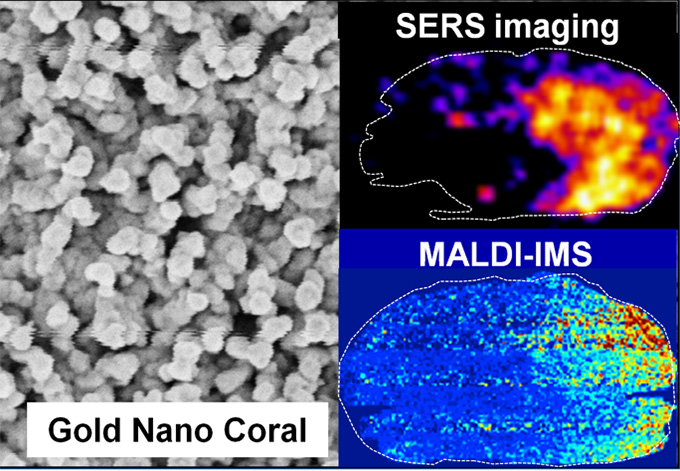
New SERS substrate enables large-area imaging
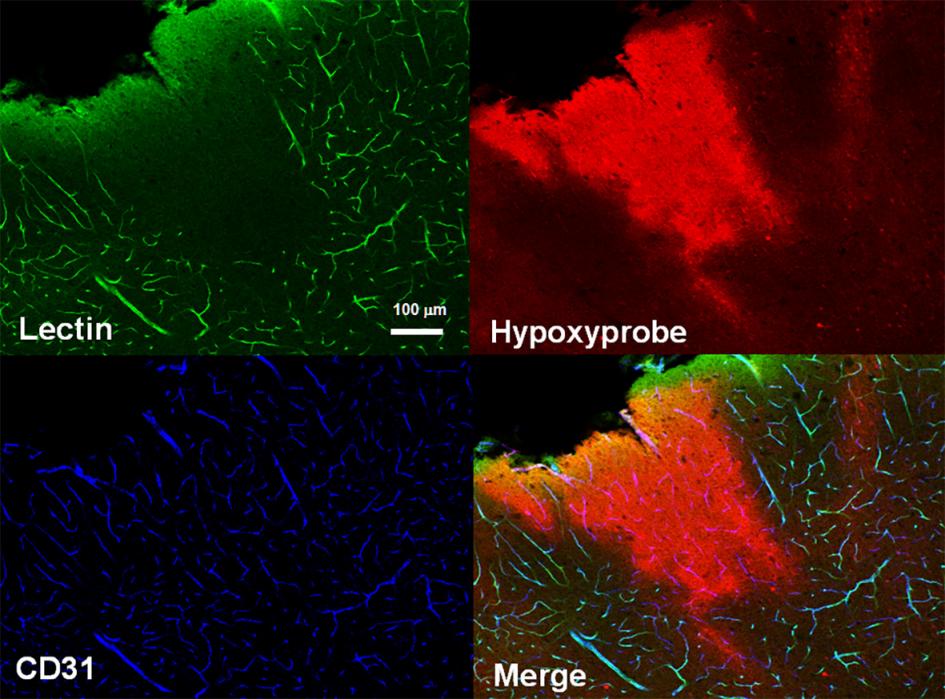
Immunohistochemical localization of patent blood vessels and hypoxic regions in the hypoxic brain
Selected Journal Publications
-
Takenouchi T, Sugiura Y, Morikawa T, Nakanishi T, Nagahata Y, Sugioka T, Honda K, Kubo A, Hishiki T, Matsuura T, Hoshino T, Takahashi T, Suematsu M, and Kajimura M. (2015) Therapeutic hypothermia achieves neuroprotection via a decrease in acetylcholine with a concurrent increase in carnitine in the neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab35(5): 794-805

-
Yamazoe S, Naya M, Shiota M, Morikawa M, Kubo A, Tani T, Hishiki T, Horiuchi T, Suematsu M, and Kajimura M.(2014) Large-area surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy imaging of brain ischemia by gold nanoparticles grown on random nanoarrays oftransparent boehmite. ACS Nano8(6): 5622-5632

-
Morikawa T., Kajimura M., Nakamura T., Hishiki T., Nakanishi T., Yukutake Y., Nagahata Y., Ishikawa M., Hattori K., Takenouchi T., Takahashi T., Ishii I., Matsubara K., Kabe Y., Uchiyama S., Nagata E., Gadalla M. M., Snyder S. H., and Suematsu M. (2012) Hypoxic regulation of the cerebral microcirculation is mediated by a carbon monoxide-sensitive hydrogen sulfide pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA109: 1293-1298

-
Nakamura T., Kajimura M., Morikawa T., Hattori K., Ishikawa M., Uchiya S., and Suematsu M. (2011) Acute CO2 -independent vasodilatation of penetrating and precapillary arterioles in mouse cerebral parenchyma upon hypoxia revealed by a thinned-skull window method. Acta Physiologica203: 187-196

-
Hattori K., Kajimura M., Hishiki T., Nakanishi T., Kubo A., Nagahata Y., Ohmura M., Yachie-Kinoshita A., Matsuura T., Morikawa T., Nakamura T., Setou M., Suematsu M. (2010) Paradoxical ATP elevation in ischemic penumbra revealed by quantitative imaging mass spectrometry. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling13: 1157-1167 (News and Views)

-
Kajimura M., Fukuda R., Bateman R. M., Yamamoto T., and Suematsu M. (2010) Interactions of multiple gas-transducing systems: Hallmarks and uncertainties of CO, NO, and H2S gas biology. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling13: 157-192 (Comprehensive Invited Review)

-
Ishikawa M., Kajimura M., Adachi T., Maruyama K., Makino N., Goda N., Yamaguchi T., Sekizuka E., and Suematsu M. (2005) Carbon monoxide from heme oxygenase-2 is a tonic regulator against nitric oxide-dependent vasodilatation in the adult rat cerebral microcirculation. Circ Res97: e104-e114 (UltraRapid Communication)

RESEARCH SYNOPSIS
My research focuses on how various gaseous molecules such as molecular oxygen (O 2), NO, H 2S, CO 2and CO are sensed in our body. We are particularly interested in the interaction between gaseous molecules and their receptor proteins, gas-sensing proteins and how these gaseous molecules modulate vascular tone in various organs. While the NO signaling has been well-defined, the CO signaling requires further investigation with respect to identifying receptor molecules and their downstream effectors. Like NO, CO has an ability to bind to the ferrous heme of a variety of proteins with high affinity; thus, it is capable of either stimulating or inhibiting catalytic activities of heme proteins. Thus in current studies we are investigating the possibility that CO targets for proteins containing prosthetic heme and by altering their activity it controls the CNS function. We use both in vivoand in vitrosystems in parallel to compensate inherent weakness of each model. This requires developing techniques which range from molecular biology, cell biology, protein biochemistry, and single vessel studies to whole animals.

 People
People